Synopsis
In the medical device industry, the margin for error is non-existent. This blog explores why laser welding has become the non-negotiable gold standard for achieving the ultra-clean, high-strength joints required for surgical instruments and implantable devices. We examine the technical necessity of hermetic sealing to protect sensitive internal electronics and ensure patient safety. A key focus is placed on the prevention of bacterial growth; we explain how the crevice-free, non-porous surface of a laser weld eliminates the microscopic hiding places where pathogens typically thrive. We also discuss how laser technology facilitates compliance with ISO 13485 standards through precise process validation and the joining of biocompatible materials like Titanium and Nitinol. By partnering with Dynotech, Indian med-tech manufacturers gain access to 100% innovative technology that ensures absolute sterility and unquestionable reliability in every life-sustaining device.
Table of Contents
-
The Zero-Tolerance Standard of Med-Tech
-
Hermetic Sealing: Protecting Life and Logic
-
Preventing Bacterial Growth: The “Clean Joint” Advantage
-
Engineering for Bio-compatibility
-
Welding Advanced Materials: Titanium, Stainless Steel, and Nitinol
-
Crevice-Free Geometry for Reliable Sterilization
-
Navigating Regulatory Waters: ISO 13485 and Validation
-
Why Dynotech? Precision That Saves Lives
The Zero-Tolerance Standard of Med-Tech
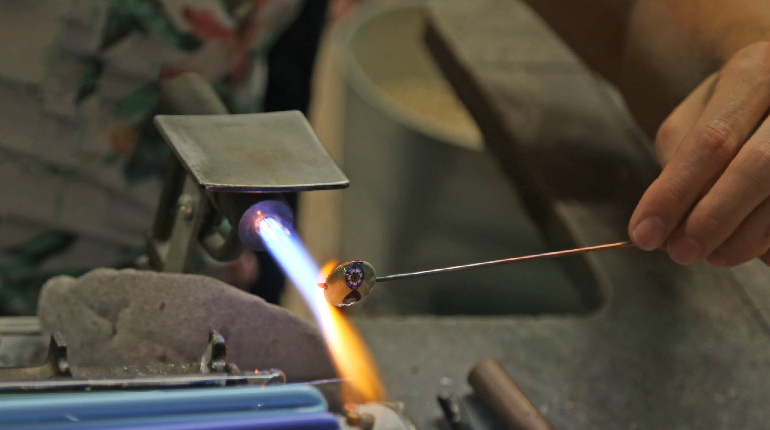
When a device enters the human body, its integrity is the only thing standing between a successful outcome and a catastrophic infection. The Zero-Tolerance Standard of Med-Tech Traditional joining methods like adhesives or TIG welding often introduce risks—chemical outgassing or excessive heat—that can compromise the device’s function. Laser welding, however, provides a non-contact, high-purity solution that has become indispensable for the modern healthcare sector.
Hermetic Sealing: Protecting Life and Logic
Hermetic Sealing: Protecting Life and Logic For active implants like pacemakers or neurostimulators, the housing must be “helium-tight.” Laser welding creates a permanent, hermetic seal that protects sensitive batteries and microelectronics from the hostile, saline environment of the human body.
Preventing Bacterial Growth: The "Clean Joint" Advantage
Preventing Bacterial Growth: The “Clean Joint” Advantage Unlike mechanical fasteners that create microscopic gaps, a laser weld is a fusion process. It produces a smooth, non-porous surface structure where germs simply cannot adhere. This eliminates crevices where bacteria could survive the sterilization process, significantly reducing the risk of post-operative cross-infection.
Engineering for Bio-compatibility
Engineering for Bio-compatibility is a fundamental requirement for any implant. The welding process itself must not introduce contaminants or alter the metal’s properties.
Welding Advanced Materials: Titanium, Stainless Steel, and Nitinol
Welding Advanced Materials: Titanium, Stainless Steel, and Nitinol These specialized alloys are chosen for their strength and compatibility with human tissue, but they are notoriously sensitive to heat. Laser welding’s ultra-low heat input preserves the metallurgical integrity of these materials, ensuring they remain bio-compatible and corrosion-resistant after joining.
Crevice-Free Geometry for Reliable Sterilization
Crevice-Free Geometry for Reliable Sterilization is particularly critical for reusable surgical instruments. Tools like laparoscopic graspers or bone reamers must undergo rigorous cleaning cycles. Because laser welds are crevice-free, they can be effectively decontaminated in far less time than traditional assemblies, ensuring that “difficult-to-clean” areas do not become a liability in the operating theater.
Navigating Regulatory Waters: ISO 13485 and Validation
Navigating Regulatory Waters: ISO 13485 and Validation Success in the medical industry requires more than just a good weld; it requires documentable proof. Laser welding systems offer superior process control, allowing for the rigorous validation (IQ/OQ/PQ) required by ISO 13485 and FDA standards. This level of repeatability ensures that the first weld and the ten-thousandth weld are identical in quality and safety.
Why Dynotech? Precision That Saves Lives
Why Dynotech? Precision That Saves Lives With 30+ years of experience, Dynotech understands the unique pressures of the medical manufacturing environment. We provide Indian healthcare innovators with 100% innovative technology and the process know-how to achieve 100% reliability. By choosing our laser welding solutions, you aren’t just improving a product; you are safeguarding human life.
FAQs
Why is laser welding better for medical devices than glue or epoxy?
Adhesives can degrade over time when exposed to body fluids or repeated sterilization cycles. Laser welding creates a permanent, molecular bond that is inherently sterile, bio-compatible, and much stronger than chemical bonding, ensuring the device remains safe for its entire lifespan.
Can laser welding join different medical-grade metals together?
Yes. Laser welding is highly effective at joining dissimilar metals, such as Titanium to Stainless Steel. The precise control of the laser energy allows for a strong metallurgical bond between different alloys, which is often impossible with traditional welding techniques.
How does laser welding help prevent hospital-acquired infections (HAIs)?
By creating a crevice-free and non-porous surface, laser welding eliminates the tiny “pockets” where bacteria can hide during the sterilization process. This ensures that surgical instruments can be 100% decontaminated, directly reducing the risk of infection.
What does "hermetic sealing" mean in medical manufacturing?
Hermetic sealing refers to a joint that is airtight and gas-tight. For implantable electronics, this is critical to prevent moisture from entering the device and to prevent potentially harmful battery chemicals from leaking into the patient’s body.
Is laser welding suitable for cleanroom environments?
Absolutely. Laser welding is a non-contact, “clean” process that produces no sparks, spatter, or milling dust. This makes it the ideal choice for assembly within a Class 10,000 or Class 1,000 cleanroom, where maintaining particle-free air is a top priority.